20+ What Do Natural Killer Cells Do In The Immune System US. It persists in the nucleus waiting until conditions are favorable. Natural killer cells, also known as nk cells or large granular lymphocytes (lgl), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system.
Then after infection, it enters inactive state that does not trigger adaptive immune response.
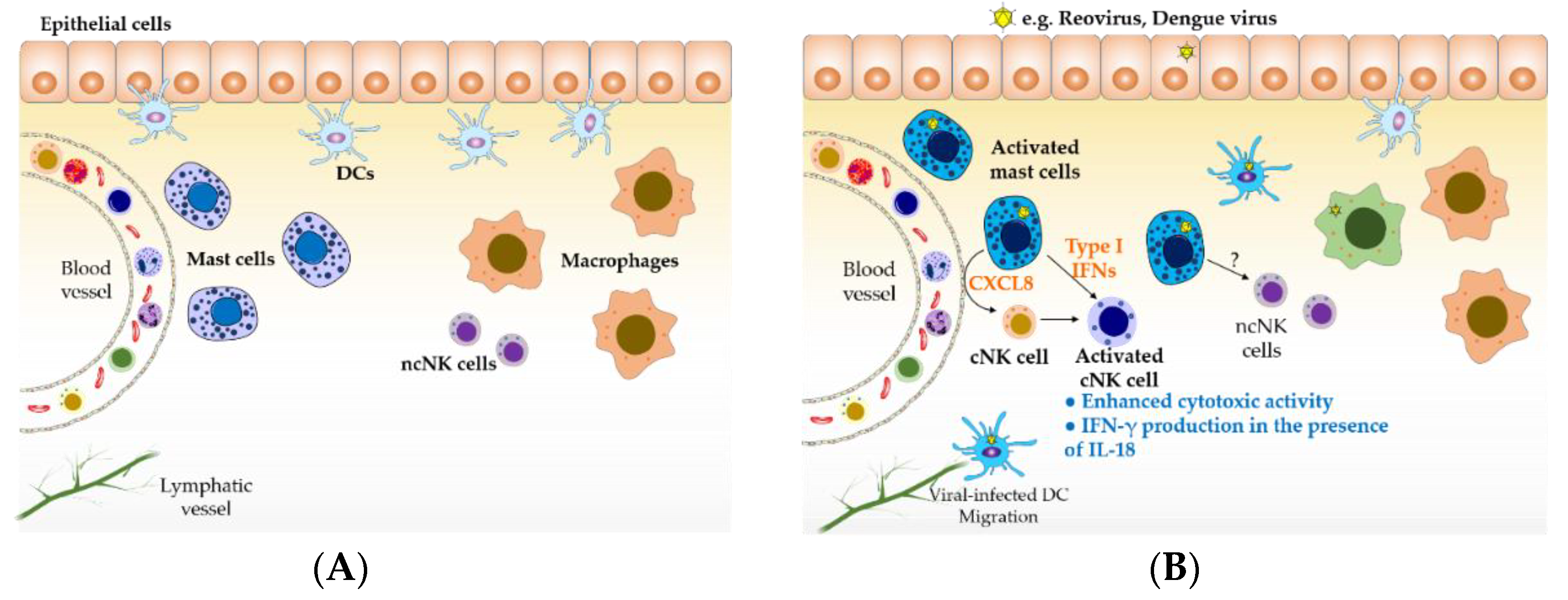
Natural killer cells (also known as nk cells, k cells, and killer cells) are a type of lymphocyte (a white blood cell) and a component of innate immune upon release in close proximity to a cell slated for killing, perforin forms pores in the cell membrane of the target cell through which the granzymes. The white blood cells are a key component. They target tumor cell and protect against a wide variety of infectious microbes. Mrna vaccines teach our cells how to make a protein—or even just a piece of a protein—that triggers an immune response inside our bodies.